KEIO: A python software to process illumina reads for keio-collection type project.
The Keio collection in Escherichia coli K-12 represents a collection of single-gene deleted mutants. This collection was created manually one by one by replacing the predicted ORF with a kanamycin cassette to inactivate chromosomal genes. Then primers were designed to create in-frame deletions upon excision of the resistance cassette. Of 4288 genes targeted, 3985 mutants were obtained. Majority of these mutants represents mutation of non-essential genes. More @
Primarily, Keio collection provides a molecular tool/resource to understand functional and physiological aspects of gene at the system levels. Although, creating such molecular collection / tools takes lot of resources and time. Thus, here we explored TnSeq methods to create a single gene mutant type collection at high-throughput scale. Once the Randomly Barcode Transposons are created, the constructs are randomly inserted into bacterial genome to create mutated clone. Each clone theoretically should represent a single gene mutation. More @
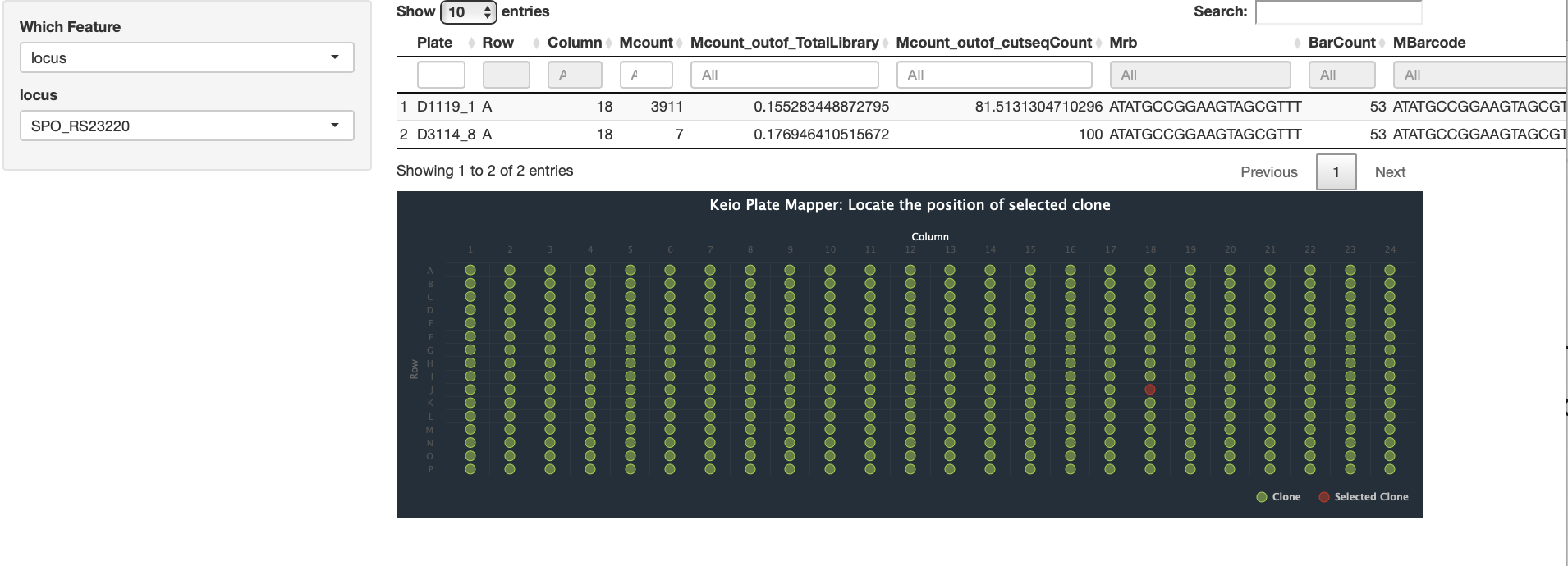
Our methods involves mapping the location of random barcode sequence (about 20 base pair in lengths) as well as inline barcodes. Mapping-positions are then mapped to the genome coordinates to identity targeted features, whereas in-line barcodes mapping allows to map the clone to specific plates ( we use 384 wells plate).
| Barcode Insertion Mapping | Plate Mapping |
|---|---|
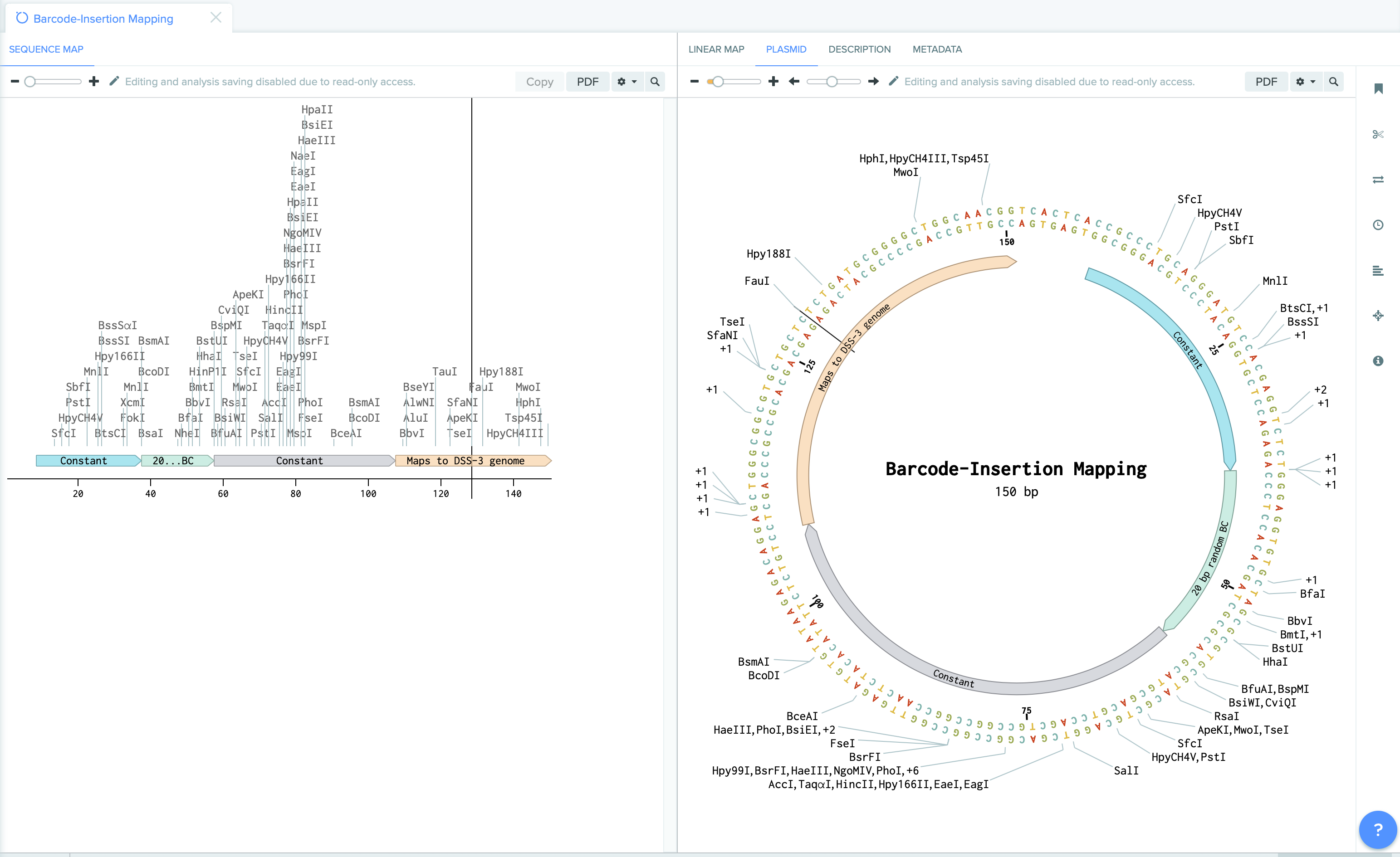 | 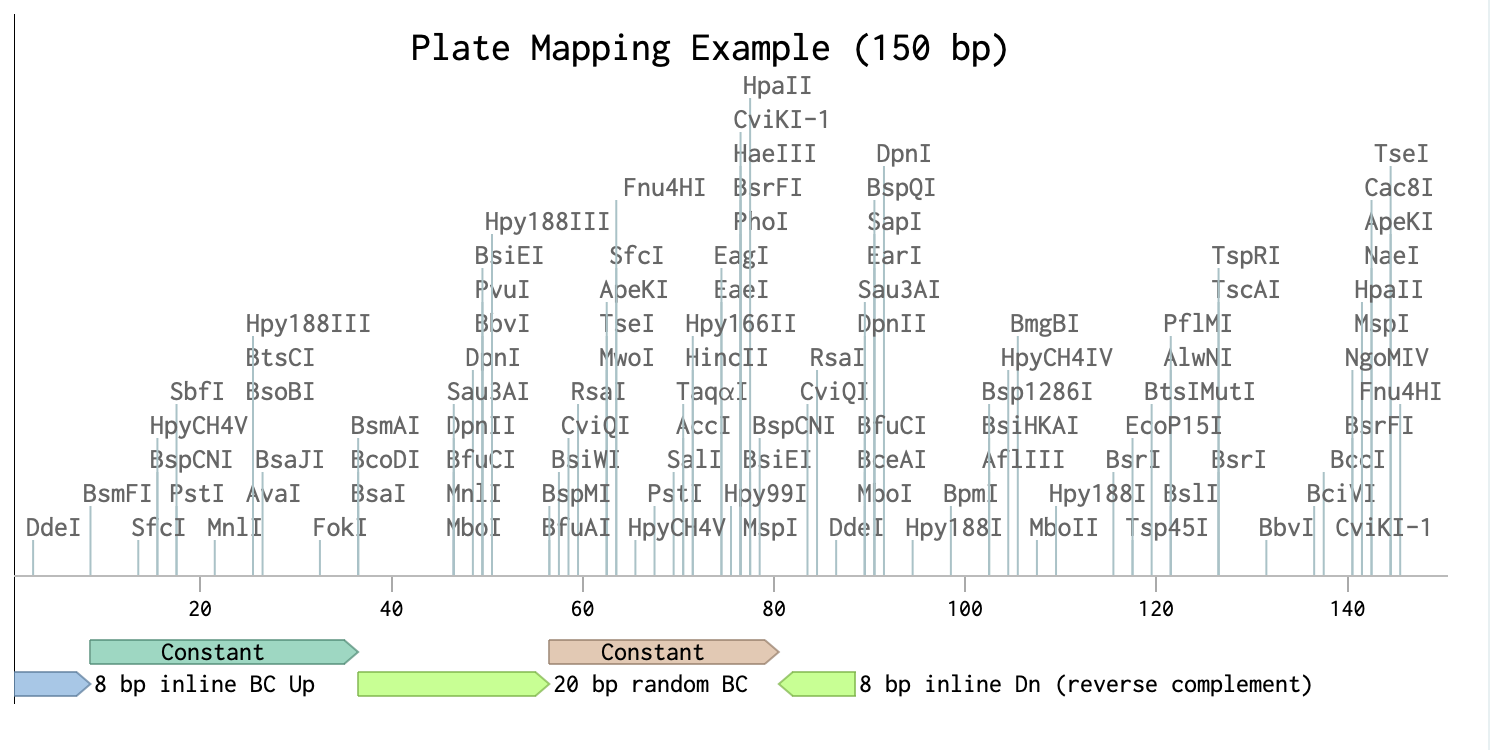 |
Authors
- Ravin Poudel, PhD, Department of Microbiology and Cell Science, University of Florida
- Adam R. Rivers, PhD , US Department of Agriculture, Agricultural Research Service
- Christopher Reisch, PhD, Department of Microbiology and Cell Science, University of Florida
Introduction
Installation
KEIO can be installed from GitHub:
# Create a conda environment and install and pybedtools
conda create -n keio python=3.7 pybedtools=0.8.2 vsearch=2.18.0
conda activate keio
git clone https://github.com/ravinpoudel/KEIO.git
cd KEIO
pip install .
# check if the installation works
keio -h
Dependencies
Following are the required softwares/programs.
VSEARCHpybedtoolsNMSLibBiopythonPandas
Usage
KEIO: A python software to process illumina reads for keio-collection type project.
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--fastq FASTQ [FASTQ ...], -f FASTQ [FASTQ ...]
input fastq file
--upstreamFasta UPSTREAMFASTA, -uf UPSTREAMFASTA
A upstreamFasta file
--downstreamrcFasta DOWNSTREAMRCFASTA, -drcf DOWNSTREAMRCFASTA
A downstreamFasta file
--threads THREADS The number of cpu threads to use
--tempdir TEMPDIR The temp file directory
--keeptemp Should intermediate files be kept?
Examples
keio -f test/test_data/sample.fq.gz \
-uf test/test_data/upstream.fasta \
-drcf test/test_data/downstream_rc.fasta \
--threads 8
Once you have output from keio, we will be using R script to process the output.
Inputs needed for Rscript
- output from Random Barcode TnSeq method, which includes the 20-bp barcode and insertion location in the chromosome. This output was generated following https://bitbucket.org/berkeleylab/feba/src/master/
Eg. DSS3BlPl.txt
- Read more at
Inplate_tag_mapping.html
mkdir results
Rscript script/keio.R sample.csv
Above script run one output at a time. If you have multiple fasta file to map, we can write a bash script/loop to run keio. Running keio can be done locally, as it should not take long time. Running Rscript might take longtime, depending on the totoal number of matches. Running as a SLURM array job will be helpful. Following is the slurm script.
script/run.sh
#!/bin/bash
#SBATCH --account="gbru_fy21_tomato_ralstonia"
#SBATCH --job-name=keio
#SBATCH --out=keio_%A_%a.log
#SBATCH --time=14-00:00:00
#SBATCH --array=1-58
#SBATCH -p atlas
#SBATCH -N 1
#SBATCH -n 48
#SBATCH --mem 250G
date;hostname;pwd
# load the required programs
# hpg1-compute
#module load conda
#source activate keio
RUN=${SLURM_ARRAY_TASK_ID}
echo "My Slurm RUN_ID: '${RUN}'"
echo "My TMPDIR IS: " $TMPDIR
# here a folder called keio_output contains all the csv's after running keio(python script)
infile=$(ls keio_output/*.csv | sed -n ${RUN}p)
echo "$infile"
time Rscript keio.R $infile
Above R script saves the result within a folder called "results". Now we have processed each fastq files and retrived the summarized information, we can copy the whole folder "results" to the local machince (laptop) and process in R using script/process.R script. This script will read in all the output from "results" folder and additionally also need files:
- DSS3_gff.csv
- output from Random Barcode TnSeq method, which includes the 20-bp barcode and insertion location in the chromosome. This output was generated following https://bitbucket.org/berkeleylab/feba/src/master/
Eg. DSS3BlPl.txt
- NC_003911.gff – this is updated gff file with updated locus information.
NOTE: These files are very specific to DSS3 genome, and the script has to be optimized depending on the genomes being analyzed.
script/process.R